Goal
Our primary goal with WobotRelay is to make device onboarding and distributed fleet management
effortless and hassle-free.
One Tool for everthing you need whether it's Edge AI or the Cloud AI processing.
Onboarding Made Easy. No Hassle. One tool for
We aim to enable true one-click device onboarding—whether it's for the Edge AI or the Cloud AI processing. Simplify your deployment process and get your devices connected and managed in no time.
Problem Statement
Stop Wrestling With SSH & Scattered Installs
Say goodbye to countless guides, tedious port-forwards, and juggling half a dozen tools just to get connected.
- Manual SSH Headaches? Endless commands, managing private keys, navigating firewalls… enough already.
- Multiple Install Guides? SmartStreamer, WMS, Hailo drivers, DT, WoPipe… one complex setup for every tool.
- Ports to Open—Every Time? Firewall rules, NAT punch-through, VPN tunnels… a constant battle for connectivity.
- Bandwidth Metrics Needed? Do you really want to constantly bug your users just to get throughput information?
- Toolchain Overload? RPort, ffmpeg, custom scripts—why complicate simple tasks with so many moving parts?
Imagine skipping all of that—and going live with a single click.
WobotRelay handles everything—from connectivity to configuration—to get your streams and commands flowing in seconds.
Overview
WobotRelay is a powerful server-client system designed to manage distributed fleets of devices with ease. It provides centralized control over remote agents, enabling configuration management, task execution, and real-time monitoring through a secure relay server.
Secure
End-to-end encrypted communication with bcrypt hashing for credentials
Real-time
Bi-directional WebSocket communication for instant updates and commands
Scalable
Designed to handle thousands of clients with efficient resource usage
LightWeight
Less than ~10mb agent size.
Key Features
- Centralized configuration management for distributed clients
- Remote command execution with real-time feedback
- Network speed testing capabilities
- Process management with automatic restart policies
- Configuration file watching and automatic reloading
- Comprehensive logging and status monitoring
- Secure authentication and authorization workflows
System Architecture
Architecture Diagram
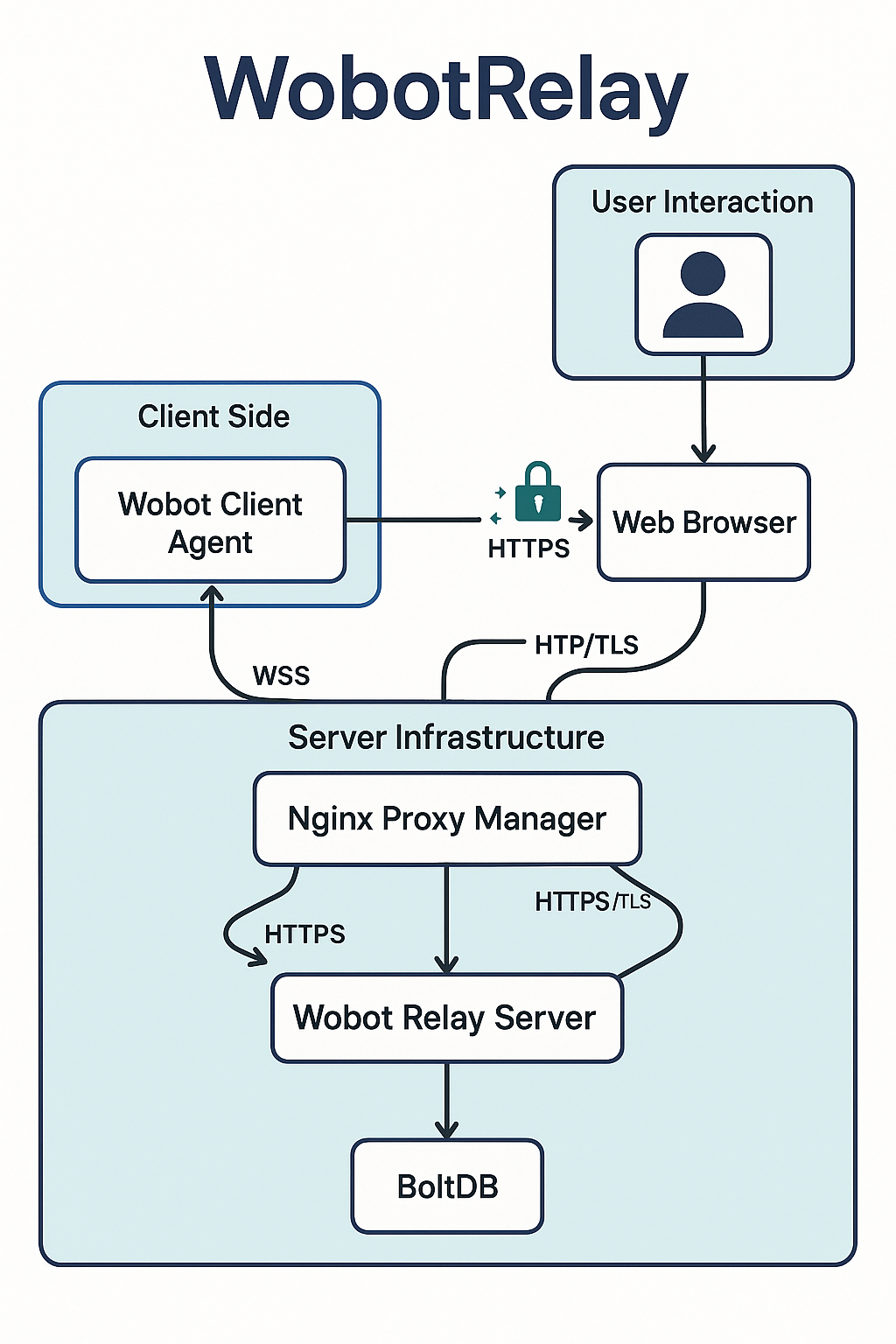
Relay Server
Admin UI
Client 1
Client 2
Client N
The WobotRelay system consists of three main components: the central Relay Server, Admin UIs for management, and multiple Client agents that connect to the server. All communication flows through the Relay Server which acts as the central hub.
Communication Flow
- Admin UI connects to the server via WebSocket using an authentication ticket
- Clients go through authentication workflow to establish persistent WebSocket connections
- Admin sends commands through their WebSocket connection
- Server routes commands to appropriate clients
- Clients execute commands and send responses back to server
- Server forwards responses to the originating Admin UI
Data Storage
Server Storage
- BoltDB embedded key-value database
- User groups and hashed handshake keys
- Client configurations and status
- Admin API keys
- Temporary request states
Client Storage
- config.yaml file for local configuration
- WobotRelay.log for local logging
- Runtime state in memory
Server Component
The WobotRelay server acts as the central hub for all communication between admin interfaces and client agents. It handles authentication, message routing, and state management for the entire system.
Core Components
Hub
- Manages active WebSocket connections
- Uses channels for safe client registration/unregistration
- Manages client status (Online/Offline)
- Holds reference to BoltDB instance
Admin Connections
- Separate from regular client connections
- Authenticated using short-lived tickets
- Each has dedicated adminWsReader goroutine
Database
- BoltDB embedded key-value store
- Buckets for UserGroups, Clients, AdminKeys, etc.
- All operations within transactions
Message Routing
- Uses correlation IDs for request/response matching
- PendingTests map for speed test orchestration
- Cleanup goroutines for stale data
Server Endpoints
| Endpoint | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| /ws | GET | Initial client handshake endpoint |
| /ws/status/:requestID | GET | Client polling endpoint for approval status |
| /ws?clientID=... | GET | Persistent WebSocket connection for clients |
| /ws/admin?ticket=... | GET | WebSocket connection for admin UIs |
| /api/auth/ws-ticket | POST | Generates WebSocket tickets for admin UIs |
Server Message Types
From Clients
- config_update - Client configuration updates
- speed_test_result - Speed test results
- Ping - Connection keep-alive
To Clients
- set_name - Update client name
- add_path - Add new path configuration
- delete_path - Remove path configuration
- reload_config - Trigger config reload
- trigger_speedtest - Initiate speed test
Client Component
The WobotRelay client is a managed agent that connects to the central server, executes commands, and reports status. It handles local process management and can perform tasks like speed tests when requested.
Client Lifecycle State Machine
The client progresses through these states during its lifecycle, with potential transitions back to earlier states when errors occur or when re-authentication is needed.
Core Components
AppState
- Central coordinator for client state
- Manages application context for shutdown
- Handles WebSocket connection lifecycle
- Manages cleanup functions
AppConfig
- Maps to config.yaml file
- Stores client credentials and settings
- Contains Paths configuration
Command & CommandPool
- Manages external process execution
- Handles automatic restart with backoff
- Process group management for clean termination
ConfigWatcher
- Monitors config.yaml for changes
- Uses debouncing to avoid rapid reloads
- Triggers automatic reload when config changes
Configuration File (config.yaml)
name: "Client-1"
handshakeKey: "group-default123"
clientID: "" # Will be populated after approval
clientSecret: "" # Will be populated after approval
logLevel: "info"
commandRestartMaxDelay: "5m"
paths:
service-A:
runOnInit: "/usr/bin/my-service --config /etc/my-service.conf"
runOnInitRestart: "yes" # Restart if it crashes
environment:
- "ENV=production"
- "LOG_LEVEL=debug"
backup-job:
runOnInit: "/usr/local/bin/backup --daily"
runOnInitRestart: "no" # Only run once on start
Client Message Handling
From Server
- set_name - Updates client name in config
- add_path - Adds new path configuration
- delete_path - Removes path configuration
- reload_config - Triggers config reload
- trigger_speedtest - Initiates speed test
To Server
- config_update - Sends current configuration
- speed_test_result - Reports speed test results
- Ping - Connection keep-alive
Authentication Workflows
Client Authentication Flow
- Initial Handshake: Client sends GET to /ws with X-Handshake-Key header
- 202 Accepted: New request, server provides RequestID
- 409 Conflict: Existing request, server provides RequestID
- 401/403: Authentication failed
- Polling: Client polls /ws/status/:requestID with X-Handshake-Key
- 200 Approved: Server provides ClientID and ClientSecret
- 200 Pending: Continue polling
- 200 Rejected: Authentication rejected
- 404: Invalid RequestID
- Connection: Client establishes WebSocket to /ws?clientID=... with X-Client-Secret
- Success: Persistent connection established
- 401/403: Authentication failed, return to handshake
Admin Authentication Flow
- REST API: Admin uses Authorization: Bearer <admin_key> header
- WebSocket Ticket: Admin requests ticket via /api/auth/ws-ticket
- Single-use, short-lived ticket generated
- WebSocket Connection: Admin connects to /ws/admin?ticket=...
- Ticket validated and consumed
- Persistent connection established
Security Considerations
Handshake Key Security
The initial handshake key should be treated as sensitive and ideally rotated periodically or used for temporary client registration only.
Client Secret Security
Client secrets are long-lived credentials for persistent connections. They should be stored securely on the client and server.
Admin Key Security
Admin API keys grant significant control. They should be protected and used over HTTPS. WebSocket tickets provide a safer alternative for direct WebSocket connections.
TLS/SSL
Always deploy the Relay Server with TLS/SSL enabled to ensure all communication is encrypted in transit.
API Reference (WebSocket Messages)
Communication between the Admin UI/API and the Relay Server, and between the Relay Server and Clients, is primarily handled via WebSocket messages. Messages follow a standard JSON structure.
Message Structure
{
"type": "message_type", // e.g., "command", "config_update", "speed_test_result"
"correlationID": "unique_request_id", // Used to match requests and responses
"clientID": "target_client_id", // Optional: Specifies target client for server->client messages
"payload": {
// Message-specific data
}
}
The correlationID is crucial for asynchronous communication, allowing the sender to associate a response message with its original request.
Common Message Types
Admin to Server
- list_clients: Request list of connected clients. Payload: {}
- get_client_config: Request config for a specific client. Payload: { "clientID": "..." }
- update_client_config: Send config update to a client. Payload: { "clientID": "...", "config": { ... } }
- execute_command: Send command to a client. Payload: { "clientID": "...", "command": "...", "args": [...] }
- trigger_speedtest: Request speed test on a client. Payload: { "clientID": "..." }
- approve_client: Approve a pending client. Payload: { "requestID": "...", "clientID": "...", "clientSecret": "..." }
- reject_client: Reject a pending client. Payload: { "requestID": "..." }
Server to Admin
- client_list: Response to list_clients. Payload: { "clients": [...] }
- client_config: Response to get_client_config. Payload: { "clientID": "...", "config": { ... } }
- command_output: Output from execute_command. Payload: { "clientID": "...", "output": "...", "exitCode": 0 }
- speed_test_result: Result from trigger_speedtest. Payload: { "clientID": "...", "download": ..., "upload": ... }
- client_status_update: Notification of client status change (connected/disconnected). Payload: { "clientID": "...", "status": "online" | "offline" }
- new_client_handshake: Notification of a new client requesting approval. Payload: { "requestID": "...", "handshakeKey": "..." }
- ack: Acknowledgement for certain commands. Payload: { "status": "ok" | "error", "message": "..." }
This is not an exhaustive list. Refer to the server source code for the complete set of message types and their payloads.
Examples
Client config.yaml
A basic client configuration file looks like this:
serverAddress: "wss://your-relay-server.com/ws"
handshakeKey: "your-initial-handshake-key"
clientID: "" # Will be populated after approval
clientSecret: "" # Will be populated after approval
logLevel: "info"
commandRestartMaxDelay: "5m"
paths:
# Define processes to manage
my-app-service:
runOnInit: "/opt/my-app/start.sh"
runOnInitRestart: "yes" # Restart if it crashes
environment:
- "APP_ENV=production"
data-collector:
runOnInit: "/usr/local/bin/collect-data"
runOnInitRestart: "no" # Only run once on start
The clientID and clientSecret fields are initially empty and are populated by the server during the authentication and approval process.
Sending a Command (Admin API/UI)
To execute a command on a specific client via the WebSocket API, you would send a JSON message like this:
{
"type": "execute_command",
"correlationID": "cmd-xyz123", // Unique ID for this request
"clientID": "client-abc-123", // The ID of the target client
"payload": {
"command": "ls",
"args": ["-l", "/home/user"]
}
}
The server would then route this message to the client with ID "client-abc-123". The client would execute ls -l /home/user and send back a command_output message with the same correlationID.
Updating Client Configuration (Admin API/UI)
To update a client's configuration, send an update_client_config message:
{
"type": "update_client_config",
"correlationID": "cfg-update-789",
"clientID": "client-abc-123",
"payload": {
"config": {
"logLevel": "debug",
"paths": {
"my-app-service": {
"runOnInit": "/opt/my-app/start.sh",
"runOnInitRestart": "yes",
"environment": [
"APP_ENV=staging" // Change environment variable
]
}
}
}
}
}
The client will receive this update, save it to its local config.yaml, and trigger a reload if necessary (or if reload_config is sent).